How Long Should You Fast for Weight Loss

Fasting has gained popularity as a weight loss strategy, but understanding “How Long Should You Fast for Weight Loss” is essential for safety and effectiveness. This guide delves into various fasting methods, health considerations, and practical tips specifically tailored for women.
Many studies have examined how well fasting works for weight loss. A systematic review published in the Journal of Translational Medicine found that intermittent fasting can lead to significant weight loss. It also improves key health markers like insulin sensitivity and cholesterol levels. These findings show that fasting can be a good strategy for managing weight and improving overall health.
Exploring Various Fasting Methods
Intermittent Fasting (IF)
Intermittent fasting (IF) includes alternate periods of fasting and eating. It’s flexible and can be adapted to suit individual lifestyles and preferences. Let’s explore some common methods:
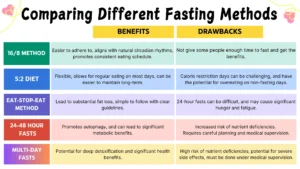
- 16/8 Method: This is an 8-hour window for eating and a 16-hour fast. For instance, you might eat from noon to 8 PM and fast until noon the next day. This method is popular because it aligns with the body’s natural circadian rhythm and is easier to maintain over the long term.
- 5:2 Diet: In this approach, you eat normally five days a week and restrict your calorie intake to about 500-600 calories on two non-consecutive days. Studies indicate that this flexibility can result in significant weight loss and better health markers, and it can be easier to follow than daily calorie restriction.
- Eat-Stop-Eat Method: The method requires one or two 24-hour fasts every week. For example, you might finish dinner at 7 PM and not eat again until 7 PM the following day. This approach can be challenging but may offer profound benefits for those who manage it, including improved fat metabolism and weight loss.
Research shows that the 16/8 method can help reduce body weight and improve metabolic health markers such as insulin sensitivity and blood lipid levels.
Extended Fasting
Extended fasting involves fasting for longer periods, typically 24 to 72 hours or more. These fasts are more intensive and should be approached with caution:
- 24-48 Hour Fasts: These fasts require more preparation and caution. During this time, your body shifts from burning glycogen to burning fat for energy. Benefits include improved insulin sensitivity and cellular repair through a process known as autophagy. However, potential side effects like dizziness and fatigue should be monitored.
- Multi-Day Fasts: Fasts extending beyond 48 hours are considered multi-day fasts. These should be done under medical supervision due to the risk of nutrient deficiencies and other health complications. While some studies indicate benefits such as improved metabolic health and reduced inflammation, the risks and challenges are significant.
How Long Should You Fast for Weight Loss
Comparing Methods
There are several fasting methods, each with its benefits and drawbacks. Understanding these can help you decide which approach suits you best.
Choosing the Right Method
Choosing the appropriate fasting method depends on your goals, lifestyle, and health conditions. Consider the following factors when choosing a fasting regimen:
- Define your primary objective, improved metabolic health, or other benefits.
- Choose a method that fits seamlessly into your daily routine. For instance, the 16/8 method might be more manageable, if you have a busy schedule.
- If you have any medical conditions, consult a healthcare provider to determine the safest and most effective fasting method.
- Opt for a method you can maintain long-term. A sustainable approach will yield better results over time.
- Start with a less restrictive method and monitor how your body responds. Adjust your fasting plan as needed to align with your health and well-being.
By comparing the benefits and drawbacks of each fasting method and considering your circumstances, you can find the fasting regimen that best supports your weight loss goals and overall health.
Practical Tips for Fasting
Personal Goals
Tailor your fasting regimen to align with your weight loss goals, lifestyle, and preferences.
- Start with shorter fasting periods and gradually increase duration as your body adjusts.
- For instance, intermittent fasting might be more sustainable than extended fasting if your goal is to lose weight.
- Tracking progress and adjusting your body’s response can help achieve optimal results.
Meal Planning
Effective meal planning is crucial for successful fasting.
- Focus on nutrient-dense foods during eating windows to ensure balanced nutrition.
- To support your body’s needs, incorporate a variety of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Preparing meals in advance can help you stay on track and avoid impulsive, unhealthy choices.
Managing Hunger
- Hunger can be a significant challenge during fasting periods.
- Strategies to manage hunger include staying hydrated, consuming fiber-rich foods, and incorporating low-calorie snacks.
- Drinking water or herbal teas can help suppress appetite.
- Experiment with different hunger control techniques to find what works best for you.
Exercise
Incorporating regular physical activity is important, even while fasting.
- Exercise supports overall health and can enhance weight loss efforts.
- Combine cardiovascular exercise, strength training, and flexibility exercises. For example, walking, jogging, weight lifting, and yoga can be excellent additions to your routine.
- Exercise timing can also impact your fasting experience.
- Some people prefer to work out during their eating windows, while others find that exercising in a fasted state boosts fat burning.
Flexibility
Flexibility is key when experimenting with fasting. If a particular method doesn’t suit you, don’t hesitate to explore alternatives. The objective is to identify a long-term strategy that promotes your health and well-being. For example, if the 16/8 method feels too restrictive, you might try the 5:2 diet. Listening to your body and being willing to adapt your fasting regimen can lead to long-term success.
Fasting Impact on Women’s Health

Hormonal Balance
Fasting can affect hormonal balance, which is particularly important for women. Hormones such as estrogen and progesterone boost reproductive health and overall well-being. Research suggests intermittent fasting can influence hormone levels, potentially affecting menstrual cycles.
Some women may experience irregular periods or changes in cycle length. Monitoring these changes and consulting with a healthcare provider if significant alterations occur is essential.
Bone Health
Women are at higher risk for osteoporosis, making bone health a critical consideration during fasting.
- Ensuring adequate calcium and vitamin D is vital to support bone health.
- Eat foods fortified with nutrients, leafy greens, and dairy products for healthy bones.
- Weight-bearing exercises such as walking and strength training, can also help improve bone density.
Relationship with Food
Fasting can change your relationship with food and promote a healthier mindset if approached correctly. It can help you distinguish between true hunger and habitual eating.
- It’s essential to avoid developing disordered eating patterns.
- Focus on nourishing your body with balanced meals during eating windows.
- Mindful eating practices can enhance your fasting experience and promote a positive relationship with food.
Stress and Emotional Eating
Stress and emotions significantly impact eating patterns and the success of fasting.
- Stress can trigger cravings and lead to overeating, undermining fasting efforts.
- Stress-reduction methods like exercise, mindfulness, and meditation can assist in controlling emotional eating.
- Seeking support from friends, family, or professional counselors can also provide valuable assistance in maintaining healthy habits.
Health and Safety Considerations
Medical Conditions
Before starting any fasting regimen, consult a healthcare provider, especially if you have underlying health conditions.
- Certain conditions, such as diabetes, heart disease, or eating disorders, require careful management and professional guidance.
- For example, fasting can affect blood sugar levels, which is critical for those managing diabetes.
- Tailored advice from a healthcare provider can help mitigate risks and maximize benefits.
Nutrient Intake
Fasting doesn’t mean neglecting nutrition. Maintaining adequate nutrient intake is essential to prevent deficiencies and support overall health.
- During eating windows, focus on nutrient-dense foods such as fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains.
- Studies highlight the importance of balanced meals that include all essential nutrients to sustain energy levels and promote health.
Hydration
Proper hydration is critical during fasting periods. Water, herbal teas, and broths can help maintain hydration.
- Aim to drink at least eight glasses of water daily, adjusting for activity level and climate.
- Dehydration can lead to headaches, dizziness, and other health issues, so paying attention to fluid intake is vital.
Potential Drawbacks and Challenges
Side Effects
- Fasting can cause side effects, especially during the initial adjustment period.
- Fatigue, headaches, and irritability are typical adverse effects. These are usually temporary and can be mitigated by staying hydrated and eating balanced meals during eating windows.
- Adjust your fasting regimen or consult a healthcare provider if side effects persist.
Social Situations
- Navigating social situations while fasting can be challenging.
- Social events often revolve around food and fasting regimens, which can be difficult for friends and family.
- Communicate your dietary preferences and boundaries.
- Plan for social events by bringing healthy options or eating before you go out.
- Flexibility and preparation can help you maintain your fasting regimen without feeling isolated.
Alternative Approaches
Other Diets
Fasting is not the only method for weight loss. Other dietary approaches such as the ketogenic diet, plant-based diet, or calorie counting can be effective.
Every method has benefits and drawbacks of its own.
For example, the ketogenic diet focuses on high fat and low carbohydrate intake, which can promote fat loss and improve metabolic health. Plant-based diets emphasize whole, unprocessed foods, which can enhance overall nutrition and weight loss. Calorie counting involves tracking your daily caloric intake to ensure a calorie deficit for weight loss.
Combining Methods
Combining fasting with other dietary approaches or lifestyle changes can optimize results. For example, you might combine intermittent fasting with a low-carb diet to enhance fat burning. Customize your strategy to your demands and objectives. Try out various combinations to see which one suits you the best.
Conclusion
As you embark on your fasting journey, prioritize your health and well-being. Please pay attention to your body and modify it as required. Whether you choose intermittent fasting, extended fasting, or another method, trust yourself to make decisions that align with your goals and values. With dedication, patience, and a healthy dose of self-care, you can achieve lasting success on your weight loss journey.
FAQs
What is the best fasting method for beginners?
The 16/8 method is often recommended for beginners. This approach involves fasting for 16 hours and eating during an 8-hour window. It’s easier to manage and less restrictive than other methods, making it a good starting point for those new to fasting.
Can women fast during their menstrual cycle?
Yes, women can fast during their menstrual cycle. But some women might feel more fatigued or experience increased hunger. Adjusting the fasting schedule or taking a break during particularly challenging days might be helpful. Consult with a healthcare provider for personalized advice.
How long does it take to see results from fasting?
Results don’t always show up right away for different people. Some people may notice changes in weight and energy levels within a few weeks, while others might take longer. Consistency and adherence to a healthy eating plan during eating windows are crucial for seeing results.
What should I eat during my eating windows?
Focus on nutrient-dense foods during eating windows. Add an abundance of entire grains, fruits, veggies, lean proteins, and healthy fats to your diet. Avoid processed foods, sugary snacks, and excessive amounts of refined carbs to maximize the benefits of fasting.
Is it safe to exercise while fasting?
Yes, it is generally safe to exercise while fasting. However, it’s important to pay attention to how your body feels. Some people may prefer to exercise during their eating windows, while others find that working out in a fasted state enhances fat burning. Start with light to moderate exercise and gradually increase intensity as your body adapts.
Can I drink water, coffee, or tea during fasting periods?
You can drink water, coffee, and tea during fasting periods. Water and herbal teas are encouraged to maintain hydration. Black coffee and unsweetened tea are also acceptable, but avoid adding sugar, milk, or cream as they can break your fast.
What are the potential side effects of fasting?
Common side effects include headaches, fatigue, irritability, and dizziness, especially during the initial stages. These symptoms often subside as your body adjusts to the fasting regimen. Staying hydrated and ensuring adequate nutrient intake during eating windows can help mitigate these effects.
How can I manage hunger during fasting?
Managing hunger can be challenging. Drinking plenty of water, herbal teas, and high-fiber, nutrient-dense foods during meals can help. Distractions, like engaging in activities or hobbies can distract you from hunger.
Can fasting help with conditions like diabetes or high blood pressure?
Fasting has shown potential benefits for diabetes and high blood pressure by improving insulin sensitivity and reducing blood pressure levels. However, individuals with these conditions should consult their healthcare provider before starting a fasting regimen to ensure it’s safe and appropriate for their health needs.
What if I feel very weak or unwell during a fast?
If you feel very weak or unwell during a fast, break your fast and consume a balanced meal to stabilize your condition. Persistent or severe symptoms should be discussed with a healthcare provider to rule out underlying health problems.
How does fasting affect mental clarity and focus?
Many people report improved mental clarity and focus while fasting. This is partly due to stable blood sugar levels and the body’s shift to using ketones for energy, which can enhance brain function. However, some individuals might experience temporary brain fog, especially during the initial adjustment period.
Is it necessary to take supplements while fasting?
While not always necessary, some individuals might benefit from supplements to ensure they’re meeting their nutritional needs. Common supplements include multivitamins, vitamin D, calcium, and omega-3 fatty acids. It’s best to consult a healthcare provider to determine if supplements are appropriate.
These FAQs provide a comprehensive overview of common questions and concerns about fasting for weight loss, helping you make informed decisions on your journey.






